Written by: Liz Paton, MSc
Developmental Anatomy Overview
Developmental Anatomy is the branch of anatomy that covers the structural changes that cells, tissues, organs and the human body undergo from fertilisation to adulthood.
For some extra research, take a look at our Developmental Anatomy Poster which teams up with our Developmental Anatomy Revision Worksheet.
Before Birth
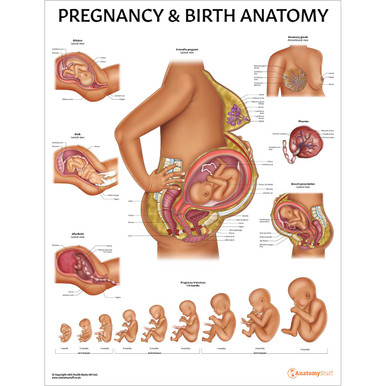
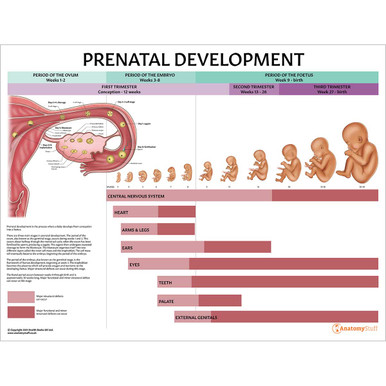
There are three main stages that take place before birth. The first one to two weeks following conception is called the germinal stage. Weeks three through eight are called the embryonic stage, and week nine up until birth is called the foetal stage. These all occur within the prenatal period. We have an addtional article that discusses pregnancy and birth in more depth.
Germinal Stage and Embryonic Development
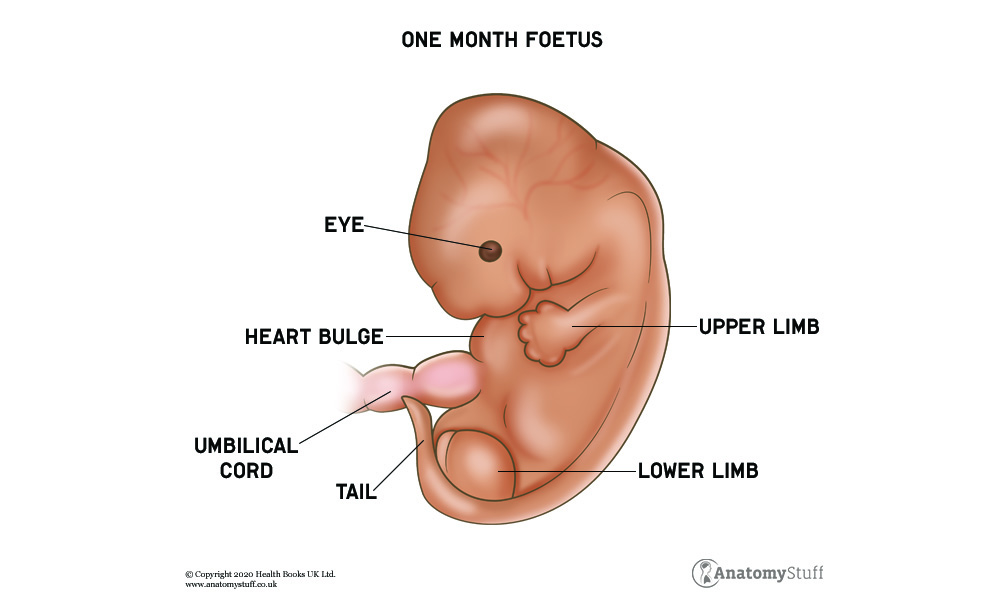
Human development starts with the germinal stage, which beings with fertilisation, the fusion of one sperm with an egg-producing a zygote (also known as a fertilised ovum). The zygote then undergoes repeated cleavage to form the blastula. The blastula organises itself into two different layers called the inner cell mass and the trophoblast. The cell mass will eventually become the embryo, thus beginning the embryonic period by week two. The embryonic period is the framework of human development. The trophoblast becomes the placenta which will provide oxygen and nutrients to the developing foetus.
Foetal Development
The foetal period begins at week nine. Between weeks nine up until birth, the foetus will undergo several changes that make it more human. The foetal period focuses on growth and development. During this period, the human brain and other organs begin to undergo important changes, and the foetus begins to increase in size as muscles and bones begin to form. By week ten, fingernails begin to grow; eyebrows and eyelids begin to present themselves by week twenty-one. By week twenty-two, the foetus reaches the age of viability, the ability to survive outside the womb, and the chances of survival increase with each passing week. The pregnancy is considered full-term by week thirty-seven, and the baby is typically born between thirty-seven and forty-one weeks of pregnancy.
After Birth
Newborn
The first four weeks of a newborn’s life is called the neonatal period of development, and changes are very rapid at this time. During this period, feeding patterns are established, and bonding begins. This is also the baby’s most fragile stage, and they are at higher risk for infection.
Newborns have 94 more bones than human adults. These extra bones fuse together over time as the child gets older until around the age of 25, where the quantity of bones will plateau to the normal 206. This is why a baby’s head is so soft and fragile.
In proportion to their size, babies and children have a large surface area greater than adults. Heat can be lost quickly in colder climates, especially through their heads, and they are also more affected by warm climates, with more chance of dehydration and overheating. The body’s natural response to temperature changes, in the form of sweating and shivering, is not as developed in children as it is for an adult. The insulating layer in the skin, the subcutaneous fat, is considerably thinner in children.
Infancy
Infancy covers the ages of one month to two years old. The baby will continue to grow rapidly, doubling in length and tripling in weight. At this stage, the baby’s fine motor skills will begin improving, and they will be able to do things such as holding a spoon and playing with toys. The baby will begin observing and reacting to the people and world surrounding them. Teeth will start developing at around six months.
Childhood
Childhood covers the ages of two years to puberty. Childhood can be broken up into three stages: early childhood, middle childhood, and adolescence. Early childhood is the time between infancy and age five. Middle childhood is the time between six and twelve years old. Adolescence is the teen years, often considered the ages of thirteen years through nineteen years old. During this time, a child will go through puberty and begin slowly transitioning into an adult.
Puberty
Puberty is the stage in life when humans become sexually mature and physical, and hormonal changes occur. This typically happens for females aged 10-14 and males aged 12-16. In females, the first stages of puberty occur when breasts and pubic hair begin to grow along with the rest of their body, and they eventually begin menstruation. In males, the first stage of puberty is the enlargement of the testicles and growth of pubic hair along with a growth spurt. Males will also notice their voices getting deeper as the larynx and vocal cords grow along with the rest of their body.
Adulthood
Development stops around the age of twenty-five years old. At this stage, the bones have fully fused, and you will have reached your plateaued height, and the brain has stopped developing.
Free Download PDFs
View AllRelated Products
View All