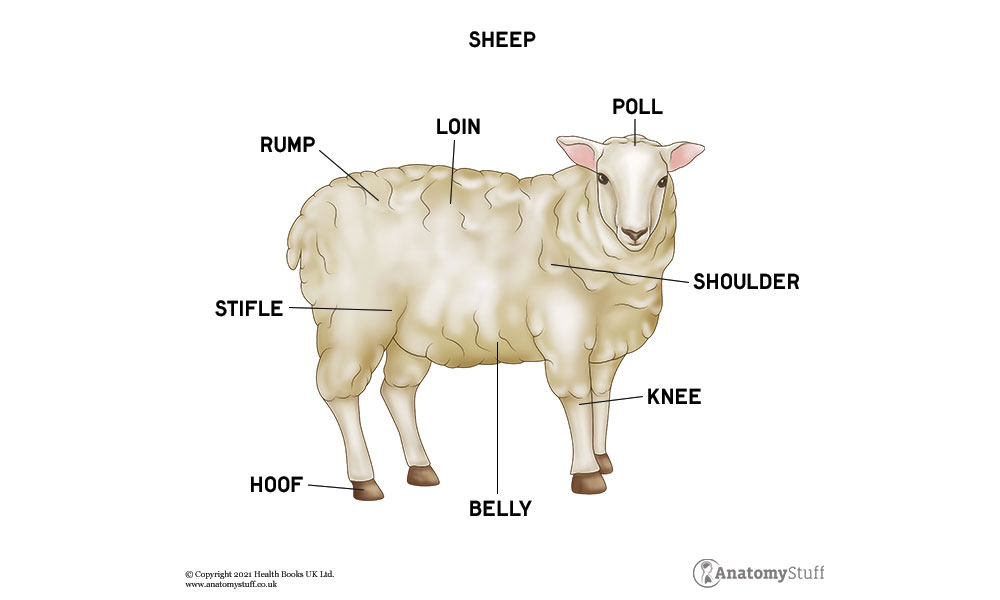
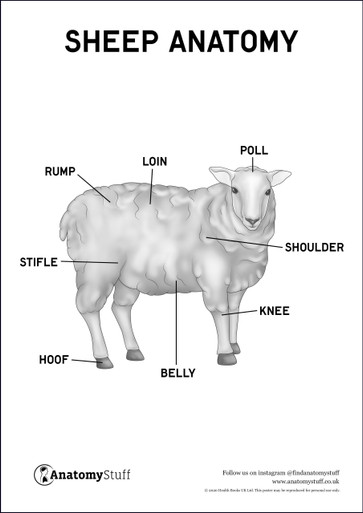
Sheep Anatomy
Sheep are ungulate mammals that have been domesticated for over 9000 years. We use sheep for wool, meat and milk. Sheep descend from wild animals known as mouflon.
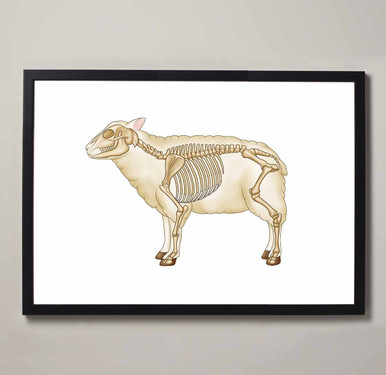
Sheep Skeleton
Sheep have 7 cervical vertebrae, 13 thoracic vertebrae, 6 lumbar vertebrae, 4 fused sacral vertebrae and between 3-24 caudal vertebrae. The skull is dome-shaped and slants downwards. Each side of the lower jaw of the sheep is held together by a ligament which allows lateral movement of the jaw when they are chewing.
The appendicular skeletal anatomy is very similar to a cow. It consists of two forelimbs and two hindlimbs. The forelimb is made up of a scapula, humerus, radius, ulnar, the carpus, metacarpals and phalanges. The hindlimb consists of the pelvic girdle which includes the ilium, ischium and pubis. The tuber coxae sits on either side of the hip bone and determines the angulation of the femur in relation to the pelvis. The femur and the tibia form the stifle joint (knee joint) and the patella sits over this joint. The rest of the hind limb consists of the fibula and the tarsus. There is a proximal, middle and distal phalanx. Each distal phalanx is contained within a hoof.
Sheep Muscles
Muscles of the Head and Neck
The orbicularis oculi muscle surrounds the eye and its function is to close the eyelids. The masseter connects the jaw bone to the cheek bone and allows the sheep to chew food in a side-to-side motion. The brachiocephalic muscle connects the base of the skull to the forelimb and allows forward movement of the forelimb and also helps to move the head and neck.
Muscles of the forelimb
The muscles which join the forelimb to the trunk include the trapezius, brachiocephalic muscle, omotransversarius, latissimus dorsi, pectoral muscles, and the rhomboids. These muscles help to transfer weight from the body to the forelimbs.
The muscles of the shoulder include the deltoid muscles, teres major, teres minor, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis and coracobrachialis. These muscles provide flexion and stability to the shoulder joint. The cervical trapezius helps to move and stabilise the scapula.
The triceps brachii extends the elbow joint. The flexors of the elbow joint are the biceps brachii and brachialis.
Muscles of the hindlimb
The biceps femoris muscle has various points of insertion and its job is to extend and abduct the hindlimb. The semimembranosus and semitendinosus help to extend the hip and the stifle joint. The medial compartment of the thigh helps with flexion and extension of the hip and adduction of the hindlimb.
The stifle joint is controlled by the quadriceps muscle. There are four muscles within this compartment which include vastus lateralis, vastus medias, vastus intermedius and the straight muscle, they extend the stifle joint and flex the hip joint. The popliteal muscle flexes the stifle joint and pronates the lower leg.
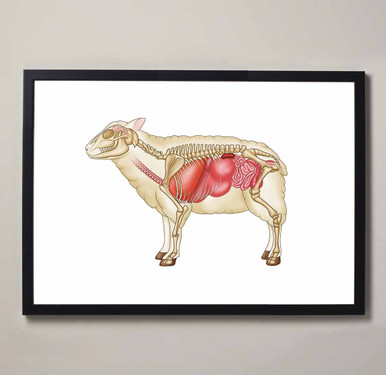
Sheep Internal Organs
Similar to cows, sheep chew their food and then regurgitate it to allow for easier digestion within the four separate compartments of the stomach.
When the food has been swallowed it enters the oesophagus which contains muscles that help transport food up to the mouth or down to the stomach. The oesophagus has this function because cows regurgitate their food where it is broken down further by the mouth.
Once the food has been broken down properly it will reach the rumen which is the first compartment of the stomach. This compartment stores chewed vegetation which is known as cud. Once the rumen absorbs some nutrients from the cud it is transported over to the reticulum. This compartment holds dense material that cannot be digested such as rocks. This material is then regurgitated as it cannot be digested. The omasum is the next compartment that helps to absorb nutrients and water. The abomasum is the last compartment that contains acid to help break down the food further.
Sheep Reproductive Organs
Ewe Reproductive Organs
The reproductive system of a ewe (female sheep) consists of the ovaries, the uterine tube, the uterus, the cervix, the vagina and the vulva.
The ovaries have an oval shape and are about 1cm in size and have the function of producing eggs and releasing oestrogen and progesterone. The fallopian tube or oviduct is where fertilisation occurs. The uterine horn is where the embryo grows and leads onto the cervix which prevents foreign bodies from entering the uterus. The cervix then leads to the vagina and then onto the vulva which is the entrance to the reproductive system.
Ram Reproductive Organs
The reproductive system of the ram (male sheep) consists of the scrotum, the testes, the vas deferens, the seminal vesicles, the prostate gland, the bulbourethral gland and the penis.
The scrotum is a sac made of muscles that contain the testes. This muscular sac helps to protect the testes and helps with temperature regulation. The testes produce testosterone which is essential for the production of sperm. The vas deferens connects the epididymis to the urethra. The prostate gland, the bulbourethral gland and the seminal vesicles are all known as accessory sex glands. These glands produce fluid that when combined with sperm produces semen. The penis deposits semen into the vagina. At the distal end of the ram’s penis is a urethral process ere the semen comes out from.
Free Download PDFs
View AllRelated Products
View All