Written by: Liz Paton, MSc
Prostate Gland Overview
The prostate gland plays an important role in the male reproductive system, responsible for releasing semen alongside fluid from other glands and the testicles. The fluid produced by the prostate gland ensures that sperm cells are transported safely for fertilisation.
Prostate Gland Anatomy
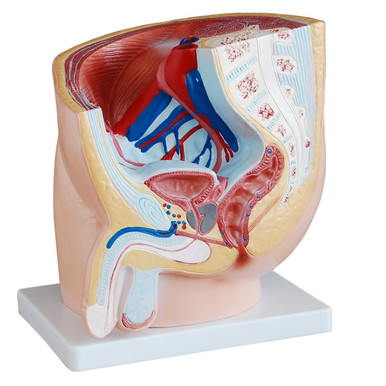
The prostate gland is about the size of a walnut, it is located below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It is surrounded by a fibrous capsule with nerves and vasculature which is covered by a layer of fascia.
Structure of the Prostate Gland
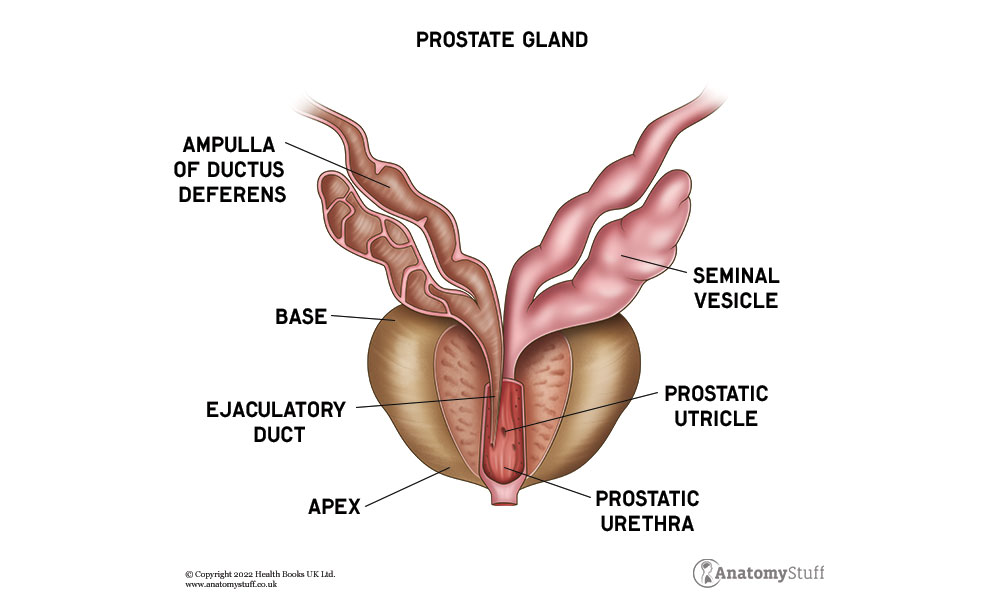
The prostate gland is divided into three zones, the peripheral zone, the central zone and the transition zone.
The peripheral zone is the outer region and occupies the back surface of the gland, this is the area where doctors will examine when they check for prostate cancer. The central zone is the surface which contains the ejaculatory ducts. The transition zone is the inner most zone and surrounds the area where the urethra enters the gland.
Blood Supply of the Prostate Gland
The blood supply of the prostate gland comes from the internal pudendal artery which also supplies other structures of reproduction. The inferior vesical artery and the middle rectal arteries also supply blood to the prostate gland. These two arteries are branches of the internal iliac artery. Venous drainage comes out of the prostatic plexus which drain into the internal iliac veins.
Nerves of the Prostate Gland
The hypogastric nerve supplies sympathetic innervation and the pelvic nerve supplies parasympathetic innervation, both of these nerves supply sensory input to the gland.
Function of the Prostate Gland
Semen is made from various fluid which the prostate gland contributes to. The fluid produced by the prostate gland is important for sperm cells from the testicles to function properly. Enzymes, proteins which speed up chemical reactions, are present in the fluid produced by the prostate gland and provide nourishment to the sperm cells.
Some enzymes make semen thinner which allows for better propulsion of the fluid during ejaculation and helps to increase the chances of fertilisation.
The fluid itself is alkaline based which provides protection for the sperm cells which enter the vagina which has an acidic environment. This helps to increase the lifespan of the sperm cells and therefore increases the chance of fertilisation.