Written by: Liz Paton, MSc
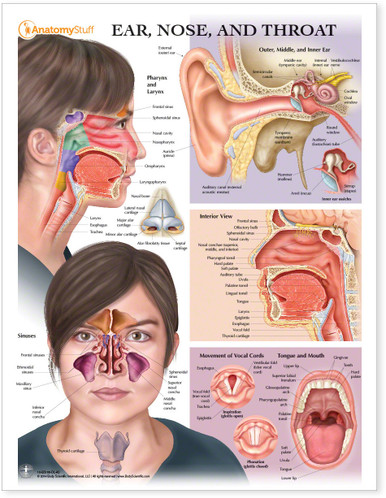
Throat Anatomy Overview
The throat is a muscular tube that allows food, liquid and air to pass through the body. The throat connects the nose and mouth to the lungs and the oesophagus (tube where food passes through). The throat has a role in helping us breathe, swallow and speak.
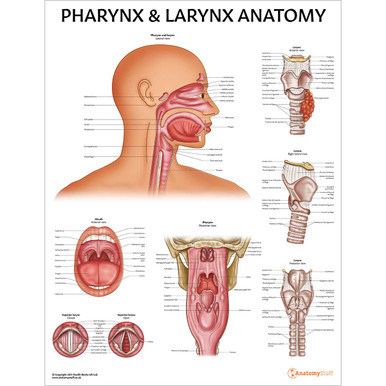
The Pharynx
The pharynx connects the nose and the mouth to the larynx and the oesophagus. The function of the pharynx is to warm the air that we take in and transports this humidified air into the lungs. The pharyngeal muscles have an important role in digestion by allowing food and liquid to pass through into the larynx.
The pharynx is made up of three parts. The nasopharynx is located behind the nasal cavity which allows air to pass through. The oropharynx is located behind the oral cavity which allows food to pass through from the mouth into the laryngopharynx. The laryngopharynx is located behind the larynx (voice box) which passes food through to the oesophagus.
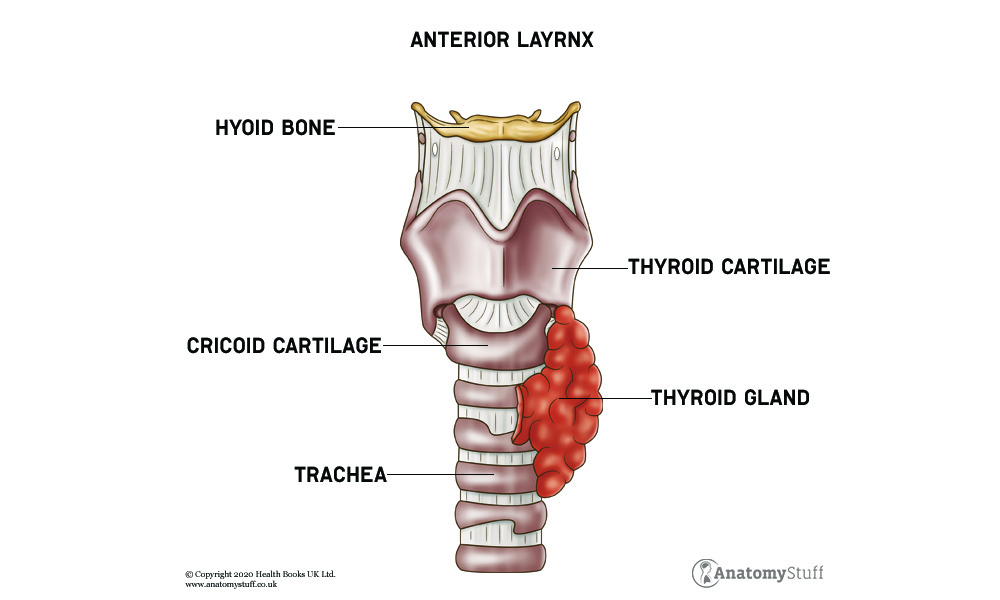
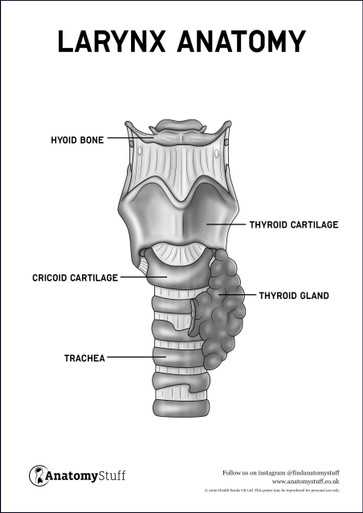
The Larynx
The larynx (voice box) contains our vocal cords and is located above the trachea (windpipe). This part of the throat is responsible for producing sound.
Speech is important for humans to communicate with each other. Speech is produced by the larynx which contains our vocal cords. When the vocal cords are relaxed, air passes through easily. When the vocal cords contract vibrations are created as air passes through. These vibrations cause us to produce sounds and form speech.
The epiglottis is a small piece of cartilage located in the upper larynx which prevent food from passing into the trachea. The larynx receives air from the laryngeal pharynx and moves into the trachea through to the lungs.
Blood Supply of the Throat
Branches of the external carotid artery supply the pharynx which includes the ascending pharyngeal, tonsillar, maxillary and lingual arteries. Deoxygenated blood is transported back to the heart through the pharyngeal veins and into the internal jugular vein.
Nerves of the Throat
The throat receives sensory and motor innervation. The pharyngeal nervous plexus innervates the throat and consists of the vagus nerve, the glossopharyngeal nerve and the maxillary nerve.