Pilates Anatomy
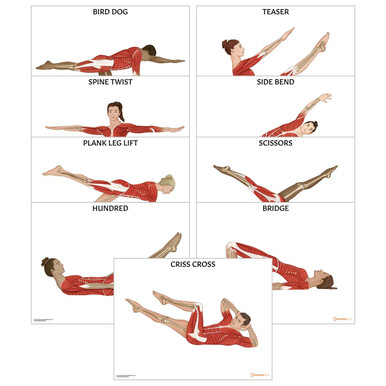
Pilates is a type of mind-body exercise developed after the late 19th-century physical culture of exercising to alleviate ill-health. However, only limited evidence supports the use of pilates in alleviating problems, such as back pain. While pilates improves balance, it has not been shown to be an effective treatment for any medical condition, but it can help muscle conditioning compared to no exercise. Pilates is a form of exercise that aims to strengthen muscles and improves postural alignment and flexibility. Pilates can be done with or without any instrument, but whatever the case may be, expect the moves to involve slow and precise movements.
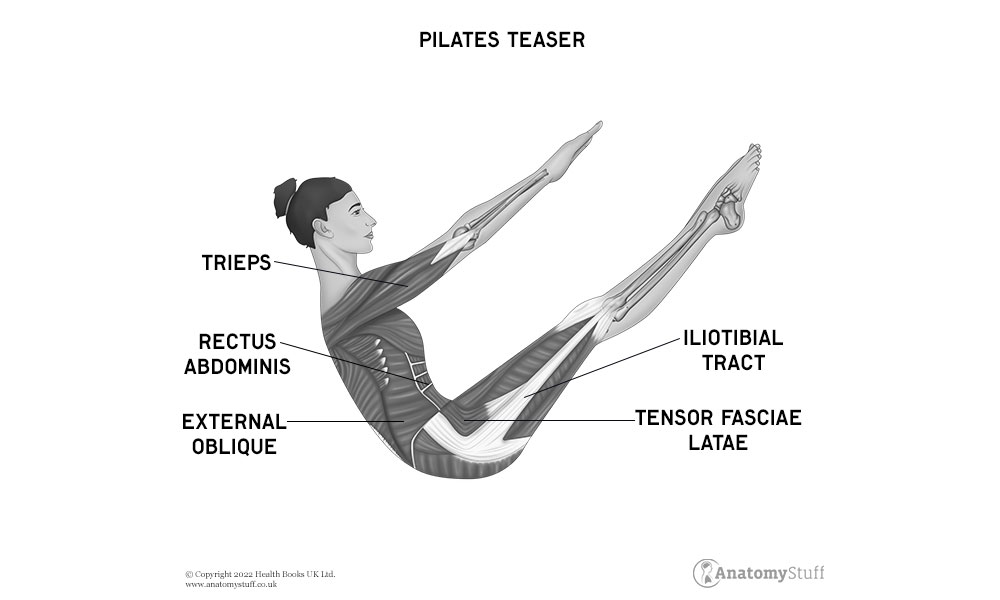
Pilates tends to target your core, although the exercises work other areas of your body as well. Although pilates may be defined as exercises for core or abdominal muscles, it is also helpful in exercising other parts of the body.
What are the benefits of pilates?
Pilates is a full-body workout that does you much good, from strengthening and stabilising your core body, to improving your posture, flexibility, and mobility. Pilates can also train you in functional movement, the kind that helps you move better on a daily basis. Some of the major health benefits of pilates are as follows:
• Improved flexibility, increased muscle strength and tone
• Balanced muscular strength and enhanced muscular control of your back and limbs
• Improved stabilisation of your spine, thus improved posture
• Improved physical coordination and balance
• Rehabilitation or prevention of injuries
• Relaxation of your shoulders, neck, and upper back
• Safe rehabilitation of joint and spinal injuries
• Prevention of musculoskeletal injuries
• Improved concentration and better body awareness
• Better stress management and relaxation.
How does pilates improve your anatomy?
Pilates increases core strength, which is all of the surrounding muscles of the trunk, which, when strengthened and pliable, support and stabilise the body. It also improves posture, which gets rid of weak, imbalanced muscles, headaches, and shoulder or back pain. Getting relief from back pain is also another benefit of pilates, as it targets the deeper abdominal muscles and the pelvic floor. Pilates also balances muscles of the body, preventing loose and weak muscles. It focuses on breathing, which increases energy and body awareness. The mind-body exercise in pilates enhances proprioception or body awareness. It can regulate your nervous system, which takes you out of fight-or-flight mode, lower cortisol, and no stress mode. Improved flexibility and mobility is also a resultant benefit of pilates. Mobility is the range of motion at a joint, while flexibility is the amount of passive stretch in a muscle. A good balance is important at any age and necessary for daily activities, pilates also improves balance and gait. Other benefits may include boosting immunity, better cognitive functioning, and improved motivation. Pilates also has a role in improving your sports performance and strengthening your bones.
Free PDF Downloads
View AllWhat is the Difference Between Yoga and Pilates?
A beginner can easily confuse certain aspects of pilates with a certain aspect of yoga. Some pilates movements can remind you of yoga, but several core differences exist. The differences can be physical and philosophical, as pilates uses breath, while yoga is a mind-body-spirit type. Stress relief also comes from other exercises, but with yoga, there’s a focus on thoughts, feelings, and actions. Both exercise forms involve balancing muscle groups and core work, but pilates focuses on much heavier core work exercises. On the other hand, yoga starts with safe alignment and safe posture.
Both these exercises complement each other, and there are some things that might be similar. There is a need for many types of equipment in yoga, but there are relatively few necessary pieces of equipment required for pilates.
Related products
View All